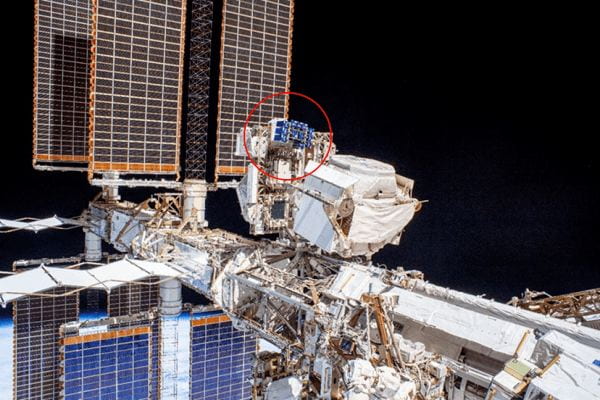
MISSE-12 is an external craft within the MISSE series aimed at testing various materials in the harsh environment of space. The crafts include ram, wake, zenith, and nadir exposures. (These are coordinate axes in the spacecraft-centered coordinate system.)
Craft Overview:
MISSE-12 was sent to the International Space Station (ISS) with three MISSE sample carriers (MSC’s). These are what house the different material samples which are to be tested in the vacuum of space. A total of 99 different samples were included aboard MISSE-11 to be tested. This increased the total number of MISSE samples to 349.
Results of the Mission:
The mission was a success. The ram and zenith MSC’s were returned to Earth aboard the SpaceX-20 Dragon capsule on April 7, 2020. The wake MSC was returned aboard the SpaceX-21 capsule on January 13, 2021.
Deployment:
MISSE-11 was taken to the ISS aboard Cygnus NG-11 on April 17, 2019. MISSE-11 was fastened onto the outside of the ISS on April 26, 2019. It was installed in the area known as the MISSE Flight Facility (MISSE-FF) near the ISS’s solar panels.
Sources and Additional Information:
- https://www1.grc.nasa.gov/space/iss-research/misse/#introduction
- https://www.nasa.gov/centers/armstrong/features/misse-11.html
- https://spaceflight101.com/dragon-spx14/misse-ff/
| Acronym | MISSE-11 |
| Full Name | Materials International Space Station Experiment – 11 |
| Size | 12U |
| Status | Inactive |
| Launch Date | April 17, 2019 |
| Principal Investigator | Jud Ready |